Authenticated gRPC service on Kubernetes
Adding basic authentication to a service hosted on Kubernetes
In our blog series on Kubernetes, we talked about buildings scalable MLOps on Kubernetes, architecture for MLOps, and solving application development. In this blog, we will talk about hosting a GRPC service on AWS EKS cluster. The process is roughly going to be the same for every Kubernetes cluster — however, we had to do some specific settings on the AWS Load balancer for this to work.
What is gRPC & our usecase
gRPC is an open-source RPC framework that can run in any environment. It is capable of efficiently connecting services within and between data centers, with the ability to plug in support for load balancing, tracing, health checking, and authentication.
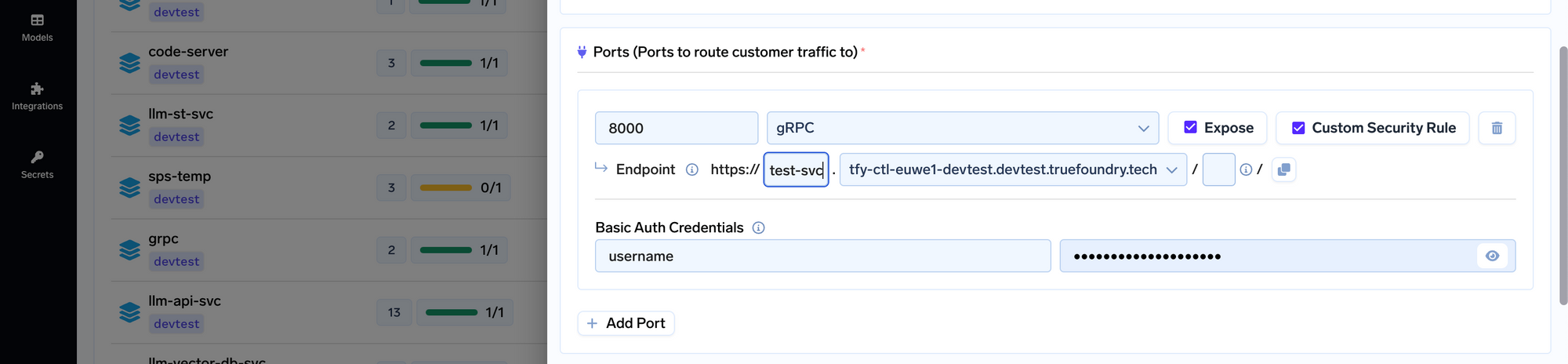
Our usecase: Hosting Tensorflow models as APIs that accepted a payload of around 100MB in size. GRPC performs much better for larger payloads — so we exposed the GRPC port on port 5000.
Hosting the service
We hosted the service on Kubernetes using the Deployment YAML below:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: ml-api
namespace: ml-services
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
truefoundry.com/component: ml-api
template:
metadata:
labels:
truefoundry.com/application: ml-api
spec:
containers:
- name: ml-api
image: >-
XXXX.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/ml-services-ml-api:latest
ports:
- name: port-8500
containerPort: 8500
protocol: TCP
resources:
limits:
cpu: '4'
ephemeral-storage: 2G
memory: 4G
requests:
cpu: '1'
ephemeral-storage: 1G
memory: 500M
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
restartPolicy: Always
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
securityContext: {}
imagePullSecrets:
- name: ml-api-image-pull-secret
schedulerName: default-scheduler
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 25%
maxSurge: 0This will bring up the pod. We need to create the Service object using the YAML below:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/instance: tfy-istio-ingress
name: tfy-wildcard
namespace: istio-system
spec:
selector:
istio: tfy-istio-ingress
servers:
- hosts:
- 'ml.example.com'
port:
name: http-tfy-wildcard
number: 80
protocol: HTTP
tls:
httpsRedirect: true
- hosts:
- 'ml.example.com'
port:
name: https-tfy-wildcard
number: 443
protocol: HTTPExposing the service
We are using Istio as the ingress layer in Kubernetes. Istio provisions a Load Balancer when the istio-ingress is installed. The load balancer configuration can be customized using annotations on the istio gateway. The spec for creating the Istio Gateway is as follows:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/instance: tfy-istio-ingress
name: tfy-wildcard
namespace: istio-system
spec:
selector:
istio: tfy-istio-ingress
servers:
- hosts:
- 'ml.example.com'
port:
name: http-tfy-wildcard
number: 80
protocol: HTTP
tls:
httpsRedirect: true
- hosts:
- 'ml.example.com'
port:
name: https-tfy-wildcard
number: 443
protocol: HTTPWe are doing the SSL termination on the AWS Load Balancer. For this we have to attach the certificate to the Load Balancer. This can be achieved using the annotations below to the istio gateway chart (https://istio-release.storage.googleapis.com/charts).
"service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-type": "nlb"
"service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-backend-protocol": "tcp"
"service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-ssl-cert": "<certificate-arn>"
"service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-ssl-ports": "https"
"service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-alpn-policy": "HTTP2Preferred"The alpn-policy is important to specify to allow GRPC traffic. Our service ml-api can be exposed by creating a VirtualService pointing to the Kubernetes service. The YAML for the Virtual Service is as follows:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/instance: ml-services_ml-api
name: ml-apiport-8500-vs
namespace: ml-services
spec:
gateways:
- istio-system/tfy-wildcard
hosts:
- ml.example.com
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: ml-api
port:
number: 8500Once the virtual service is exposed, we can make requests to our service at ml.example.com. We then wanted to add an authentication to the API so that everybody cannot call the API. We could have added the authentication in the code, but we decided to add it at the istio layer so that it can be a unified layer across all services.
To add authentication at the istio-ingress layer, we decided to go ahead with a IstioWasm Plugin. The yaml for the plugin looks something like:
apiVersion: extensions.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: WasmPlugin
metadata:
name: ml-services-ml-api-0
namespace: istio-system
spec:
phase: AUTHN
pluginConfig:
basic_auth_rules:
- credentials:
- username:password
hosts:
- ml.example.com
prefix: /
request_methods:
- GET
- PUT
- POST
- PATCH
- DELETE
selector:
matchLabels:
istio: tfy-istio-ingress
url: oci://ghcr.io/istio-ecosystem/wasm-extensions/basic_auth:1.12.0Once you have applied the above spec to the cluster, the app will ask for the username and password once you open it in the browser.
We have made it super easy on TrueFoundry
To make the above process much easier, we decide to make it really easy on the Truefoundry platform.